
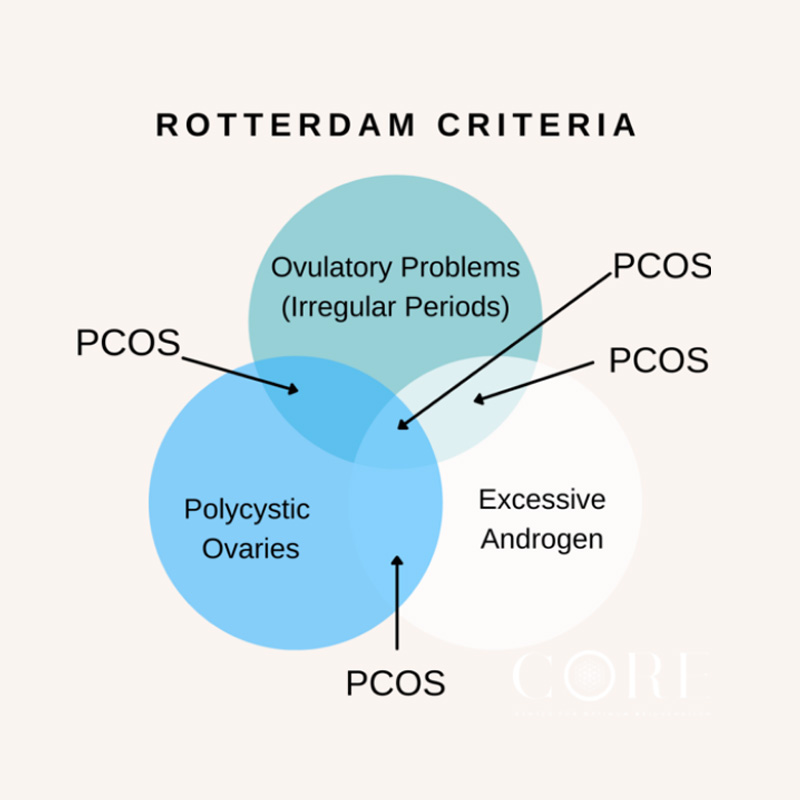
Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
This refers to infrequent or absent ovulation, which can lead to irregular periods.

What are the signs that indicate you might have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome? If you're experiencing any of the symptoms or complications associated with PCOS, it's crucial to consult a medical professional for a formal diagnosis and appropriate management. There isn't a single definitive test for PCOS. Instead, your doctor will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and, if PCOS is suspected, may conduct a pelvic exam, order blood tests, or recommend an ultrasound.

What are the Rotterdam Criteria used for diagnosing PCOS? The Rotterdam Criteria for diagnosing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) include the presence of at least two of the following three features:

This refers to infrequent or absent ovulation, which can lead to irregular periods.
This can manifest as excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, or elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) in the blood.
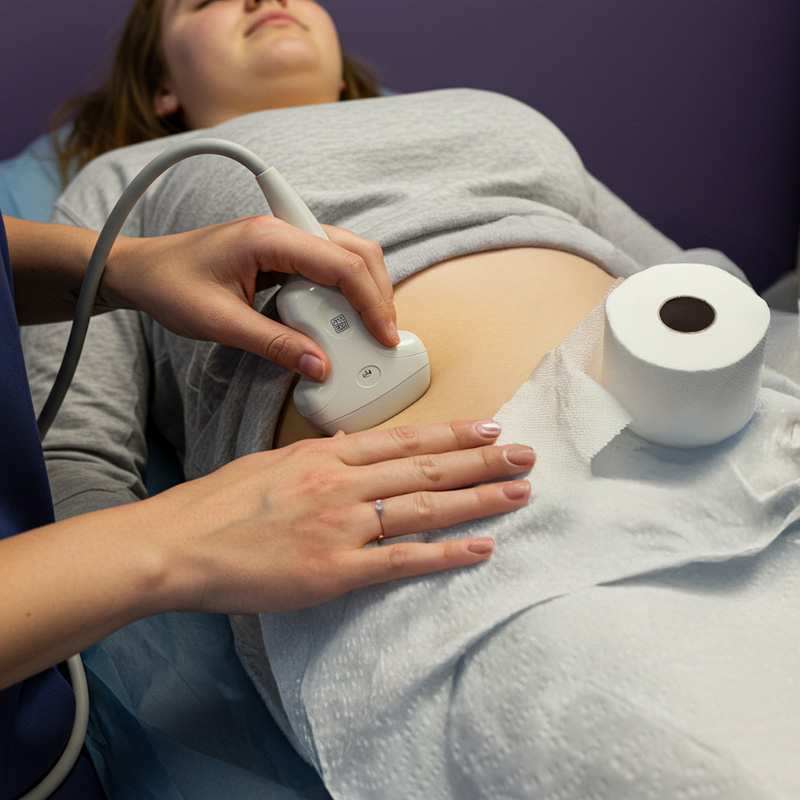
PThis is determined through ultrasound, showing the presence of 12 or more follicles in each ovary or an enlarged ovary